10. 자바 8 (Java 8) - Stream Lambda
| OS | Windows 10 Home 64bit 버전 1903 (OS 빌드 18362.836) |
| Java | 8 |
| EditTool | IntelliJ IDEA 2019.1.3 |
# 참고 사이트
Java Stream API
Stream API Java 8에서 추가된 기능으로, stream 형태의 요소에 함수형 연산자를 지원해주는 클래스이다. Stream stream은 Array, Collections와 같이 연속된 형태의 객체이다. 하지만 자료구조는 아니다. 위와 �
velog.io
Java 스트림 Stream (1) 총정리
이번 포스트에서는 Java 8의 스트림(Stream)을 살펴봅니다. 총 두 개의 포스트로, 기본적인 내용을 총정리하는 이번 포스트와 좀 더 고급 내용을 다루는 다음 포스트로 나뉘어져 있습니다. Java 스트�
futurecreator.github.io
자바 스트림(Stream) API 정리, 스트림을 이용한 가독성 좋은 코드 만들기(feat. 자바 람다, 함수형 프
Java Stream 자바 공부를 하면서 Stream이 무엇인지, 어떻게 사용되고 있는지 인지는 하고 있었으나 실제 코드로 타이핑해보지 않았다. 그러던 중 이번에 가볍게 API 훑어보는 식으로 공부를 하면서 ��
jeong-pro.tistory.com
[자바] 자바8 스트림이란?
거의 모든 자바 애플리케이션은 컬렉션을 만들고 처리하는 과정을 포함한다. 컬렉션으로 데이터를 그룹화하고 처리할 수있다. 컬렉션은 대부분의 프로그래밍 작업에 필수적인 요소다. 많은 요�
12bme.tistory.com
Java 스트림 Stream (2) 고급
이전 포스트에 이어서 Java 8의 스트림(Stream)을 살펴봅니다. 자바 8 스트림은 총 두 개의 포스트로, 기본적인 내용을 총정리하는 이전 포스트와 좀 더 고급 내용을 다루는 이번 포스트로 나뉘어져
futurecreator.github.io
# 기본
함수형 인터페이스를 이용한 선언형 프로그래밍 방식
즉, 메소드를 이용하는 방식이 아닌 필드를 선언해 이용하는 방식
선언형 프로그래밍 방식은 명령형 프로그래밍 방식보다 좋다는 말이 있다.
명령형 프로그래밍 VS 선언형 프로그래밍
명령형 프로그래밍과 선언형 프로그래밍에 대한 비교를 어디선가 한 번쯤은 접해봤을 거라 생각합니다. 그리고 그 둘이 실제로 무엇을 의미하는지 검색을 해보셨다면 아마 아래와 같은 정의를
boxfoxs.tistory.com
# 함수형 인터페이스
Stream 은 함수형 인터페이스를 이용하기 때문에 함수형 인터페이스를 알고가면 이해하기 쉽다
| 종류 | 설명 |
| 함수 (Function) | return 있는 함수형 인터페이스 |
| 서술어 (Predicate) | boolean을 리턴하는 함수형 인터페이스 |
| 비교기 (Comparator) | 두 값 간의 비교를 위해 사용하는 함수형 인터페이스 |
| 소비자 (Consumer) | return 없는 void 함수형 인터페이스 |
| 공급자 (Supplier) | return 있는 함수형 인터페이스 (인자값 없음) |
#1. Function Interface (= Setter 메소드 ?)
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| apply(인자) | Function 실행 |
| andThen(Function) | 다음 Function |
[Function 코드 1]
public class _Function {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int increment = incrementByOne(1);
System.out.println(String.format("increment = %d", increment)); // increment = 2
int f_increment = incrementByOneFunction.apply(1);
System.out.println(String.format("f_increment = %d", f_increment)); // f_increment = 2
}
private static Function<Integer, Integer> incrementByOneFunction = number -> number + 1;
private static int incrementByOne(int number) {
return number + 1;
}
}[설명]
private static Function<Integer, Integer> incrementByOneFunction = number -> number + 1;
private static Function<{{ 매개변수 타입 }}, {{ 리턴 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = {{ 매개변수 }} -> {{ 매개변수 }} + 1;
[Function 코드 2]
public class _Function {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int increment = multipleBy10(1);
System.out.println(String.format("increment = %d", increment)); // increment = 10
int f_increment = multipleBy10Function.apply(1);
System.out.println(String.format("f_increment = %d", f_increment)); // f_increment = 10
}
private static Function<Integer, Integer> multipleBy10Function = number -> number * 10;
private static int multipleBy10(int number) {
return number * 10;
}
}[설명]
private static Function<Integer, Integer> multipleBy10Function = number -> number * 10;
private static Function<{{ 매개변수 타입 }}, {{ 리턴 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = {{ 매개변수 }} -> {{ 매개변수 }} * 10;
[Function 코드 3]
public class _Function {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result1 = addByOneAndThenMultiply10(2, 10); // result1 = (2 + 1) * 10
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); // result1 = 30
Function<Integer, Integer> addByOneAndThenMultiply10Function =
incrementByOneFunction.andThen(multiplyBy10Function);
int result2 = addByOneAndThenMultiply10Function.apply(2); // result2 = (2 + 1) * 10
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); // result2 = 30
int result3 = addByOneAndThenMultiplyBi10Function.apply(2,10); // result3 = (2 + 1) * 10
System.out.println("result3 = " + result3); // result = 30
}
/** result1 function */
private static int addByOneAndThenMultiply10(int number, int numToMultiplyBy) {
return (number + 1) * numToMultiplyBy;
}
/** result2 function */
private static Function<Integer, Integer> incrementByOneFunction = number -> number + 1;
/** result2 function */
private static Function<Integer, Integer> multiplyBy10Function = number -> number * 10;
/** result3 function */
private static BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> addByOneAndThenMultiplyBi10Function =
(numberToIncrementByOne, numToMultiplyBy) -> (numberToIncrementByOne + 1) * numToMultiplyBy;
}[설명]
// andThen 은 Function의 메소드 이기 때문에 static 필드에 사용할 수 없음
Function<Integer, Integer> addByOneAndThenMultiply10Function =
incrementByOneFunction.andThen(multiplyBy10Function);
Function<{{ 매개변수타입 }}, {{ 리턴타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} =
{{ 첫 번째 실행 함수 }}.andThen({{ 두 번째 실행 함수 }});
// 2개의 인자를 넘겨줄 때는 BiFunction 을 사용한다
private static BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer> addByOneAndThenMultiplyBi10Function =
(numberToIncrementByOne, numToMultiplyBy) -> (numberToIncrementByOne + 1) * numToMultiplyBy;
private static BiFunction<{{ 매개변수 타입 }}, {{ 매개변수 타입 }}, {{ 리턴 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} =
({{ 매개변수A }}, {{ 매개변수B }}) -> ({{ 매개변수A }} + 1) * {{ 매개변수B }};
#2. Consumer Interface(=void 메소드 ?)
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| accept(인자) | Consumer 실행 |
| andThen(Consumer) | 다음 Consumer |
[Consumer 코드]
public class _Consumer {
public static class Customer {
private final String customerName;
private final String customerPhoneNumber;
public Customer(String customerName, String customerPhoneNumber) {
this.customerName = customerName;
this.customerPhoneNumber = customerPhoneNumber;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer martin = new Customer("Martin", "010-1111-1111");
// void
greetCustomer(martin);
// Consumer
greetCustomerConsumer.accept(martin);
}
/** void 메소드 */
private static void greetCustomer(Customer customer) {
System.out.println(
String.format(
"안녕하세요 %s님, 가입하신 휴대폰 번호는 %s 입니다",
customer.customerName,
customer.customerPhoneNumber
)
);
}
/** Consumer 필드 */
private static Consumer<Customer> greetCustomerConsumer = customer ->
System.out.println(
String.format(
"안녕하세요 %s님, 가입하신 휴대폰 번호는 %s 입니다",
customer.customerName,
customer.customerPhoneNumber
)
);
}[설명]
private static BiConsumer<Customer> greetCustomerConsumer = customer ->
System.out.println(...);
private static Consumer<{{ 매개변수 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = {{ 매개변수 }} ->
{{ 메소드 }}
[Consumer 코드 2]
public class _Consumer {
public static class Customer {
private String customerName;
private String customerPhoneNumber;
public Customer(String customerName, String customerPhoneNumber) {
this.customerName = customerName;
this.customerPhoneNumber = customerPhoneNumber;
}
private void setCustomerPhoneNumber(String updatePhoneNumber) {
this.customerPhoneNumber = updatePhoneNumber;
System.out.println(String.format("휴대폰 번호가 수정 되었습니다 (%s)", this.customerPhoneNumber));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer martin = new Customer("Martin", "010-1111-1111");
// void
greetCustomer(martin, false);
// Consumer
greetCustomerConsumer.accept(martin, false);
// void
updatePhoneNumberCustomer.accept(martin,"010-2222-3333");
// Consumer
updatePhoneNumberCustomer.accept(martin,"010-4444-5555");
}
/** void 메소드 */
private static void greetCustomer(Customer customer, Boolean showPhoneNumber) {
System.out.println(
String.format(
"안녕하세요 %s님, 가입하신 휴대폰 번호는 %s 입니다",
customer.customerName,
showPhoneNumber ? customer.customerPhoneNumber : customer.customerPhoneNumber.replaceAll("[0-9]", "*")
)
);
}
/** Consumer 필드 */
private static BiConsumer<Customer, Boolean> greetCustomerConsumer = (customer, showPhoneNumber) ->
System.out.println(
String.format(
"안녕하세요 %s님, 가입하신 휴대폰 번호는 %s 입니다",
customer.customerName,
showPhoneNumber ? customer.customerPhoneNumber : customer.customerPhoneNumber.replaceAll("[0-9]", "*")
)
);
/** void 메소드 */
private static void updatePhoneNumber(Customer customer, String updatePhoneNumber) {
customer.setCustomerPhoneNumber(updatePhoneNumber);
}
/** Consumer 필드 */
private static BiConsumer<Customer, String> updatePhoneNumberCustomer = Customer::setCustomerPhoneNumber;
}[설명]
private static BiConsumer<Customer, Boolean> greetCustomerConsumer = (customer, showPhoneNumber) ->
System.out.println(...);
private static BiConsumer<{{ 매개변수A 타입 }}, {{ 매개변수B 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = ({{ 매개변수A }}, {{ 매개변수B }}) ->
{{ 메소드 }}
#3. Predicate Interface
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| test(인자) | Predicate 실행 (return boolean) |
| and(Predicate) | 다음 Predicate ( && ) |
| or(Predicate) | 다음 Predicate ( || ) |
| negate() | ? |
| isEqual(인자) | 같은 |
[Predicate 코드]
public class _Predicate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 메소드
System.out.println("pn1 = " + isPhoneNumberValid("07000000000")); // true
System.out.println("pn2 = " + isPhoneNumberValid("0700000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn3 = " + isPhoneNumberValid("09000000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn4 = " + isPhoneNumberValid("07000330000")); // true
System.out.println();
// Predicate 1
System.out.println("pn1 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.test("07000000000")); // true
System.out.println("pn2 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.test("0700000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn3 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.test("09000000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn4 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.test("07000330000")); // true
System.out.println();
// Predicate 2 ( 모두 true 시 return true )
System.out.println("pn1 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.and(containsNumber3Predicate).test("07000000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn2 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.and(containsNumber3Predicate).test("0700000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn3 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.and(containsNumber3Predicate).test("09000000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn4 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.and(containsNumber3Predicate).test("07000330000")); // true
System.out.println();
// Predicate 3 ( 1개라도 true 시 return true )
System.out.println("pn1 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.or(containsNumber3Predicate).test("07000000000")); // true
System.out.println("pn2 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.or(containsNumber3Predicate).test("0700000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn3 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.or(containsNumber3Predicate).test("09000000000")); // false
System.out.println("pn4 = " + isPhoneNumberValidPredicate.or(containsNumber3Predicate).test("07000330000")); // true
}
/** 메소드 */
private static Boolean isPhoneNumberValid(String phoneNumber) {
return phoneNumber.startsWith("07") && phoneNumber.length() == 11;
}
/** Predicate 필드 */
private static Predicate<String> isPhoneNumberValidPredicate = phoneNumber ->
phoneNumber.startsWith("07") && phoneNumber.length() == 11;
/** Predicate 필드 */
private static Predicate<String> containsNumber3Predicate = phoneNumber ->
phoneNumber.contains("3");
}[설명]
private static Predicate<String> isPhoneNumberValidPredicate = phoneNumber ->
phoneNumber.startsWith("07") && phoneNumber.length() == 11;
private static Predicate<{{ 매개변수 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = {{ 매개변수 }} ->
{{ boolean }}
#4. Supplier Interface(Getter 메소드 ?)
| 메소드 | 설명 |
| get() | Supplier 실행 |
[Supplier 코드]
public class _Supplier {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 메소드 1
System.out.println(getDBConnectionUrl()); // oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users
System.out.println();
// Supplier 필드 1
System.out.println(getDBConnectionUrlSupplier.get()); // oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users
System.out.println();
// 메소드 2
System.out.println(getDBConnectionUrls()); // [oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users, ... ,mariaDb:jdbc://localhost:3306/users]
System.out.println();
// Supplier 필드 2
System.out.println(getDBConnectionUrlsSupplier.get()); // [oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users, ... ,mariaDb:jdbc://localhost:3306/users]
System.out.println();
}
/** 메소드 1 */
private static String getDBConnectionUrl() {
return "oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users";
}
/** Supplier 필드 1 */
private static Supplier<String> getDBConnectionUrlSupplier = () -> "jdbc://localhost:3306/users";
/** 메소드 2 */
private static List<String> getDBConnectionUrls() {
return Arrays.asList(
"oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users",
"mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/users",
"mariaDb:jdbc://localhost:3306/users"
);
}
/** Supplier 필드 2 */
private static Supplier< List<String> > getDBConnectionUrlsSupplier = () ->
Arrays.asList(
"oracle:jdbc://localhost:3306/users",
"mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/users",
"mariaDb:jdbc://localhost:3306/users"
);
}
[설명]
Supplier<String> getDBConnectionUrlSupplier = () -> "jdbc://localhost:3306/users";
Supplier<{{ 리턴 타입 }}> {{ 필드명 }} = () -> {{ 리턴 타입 }};
# Optional
Optional 에서도 함수형 인터페이스를 사용한다
NullPointException 처리하기 위한 클래스
| 작업 | 메소드 | 설명 |
| 오프젝트 생성 (Create Operations) |
Optional.empty() | 빈 값 |
| Optional.of(value) | 생성 NullPointException 발생) | |
| Optional.ofNullable(value) | 생성 (NullPointException 발생 x) | |
| OptionalInt.of() | int 타입으로 생성 | |
| OptionalDouble.of() | double 타입으로 생성 | |
| OptionalLong.of() | long 타입들으로 생성 | |
| 중간 연산자 (Intermediate Operations) |
.filter(Predicate) | 요소 추출 |
| .map(Function) | 요소 가공 | |
| .flatMap(Function) | 중첩 제거 가공 | |
| 최종 연산자 (Terminal Operations) |
.get() | 해당 값 |
| .orElse(value) | null 일 때 대신하는 값 | |
| .orGet(Supplier) | null 일 때 대신하는 Supplier | |
| .orThrow(Supplier) | null 일 때 Throw new Exception | |
| .isPresent() | null 이 아닐 때 true | |
| .ifPresent(Consumer) | null 이 아닐 때 Consumer | |
| .getAsInt() | int 타입 get() | |
| .getAsDouble() | double 타입 get() | |
| .getAsLong() | long 타입 get() |
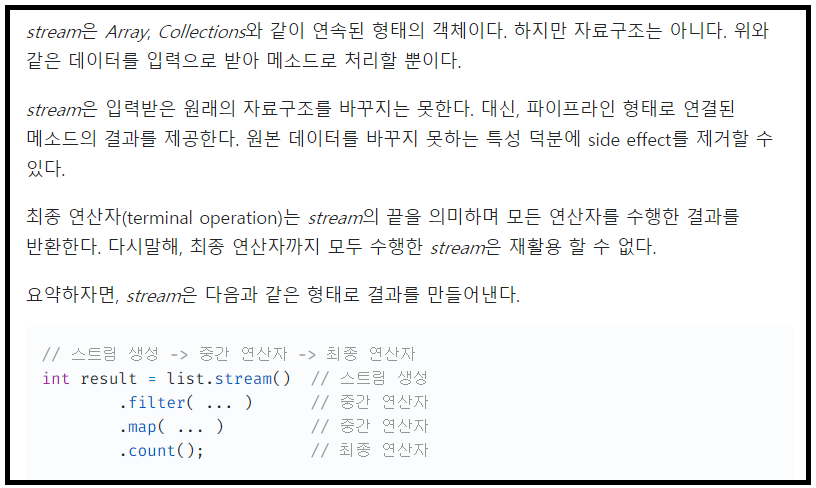
of()
Optional 객체를 생성하는 메소드
인자가 null 일 경우 NullPointerException 을 발생시킨다.
class IsPresent1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional.of(null)
.ifPresent(val -> System.out.println(val));
}
}
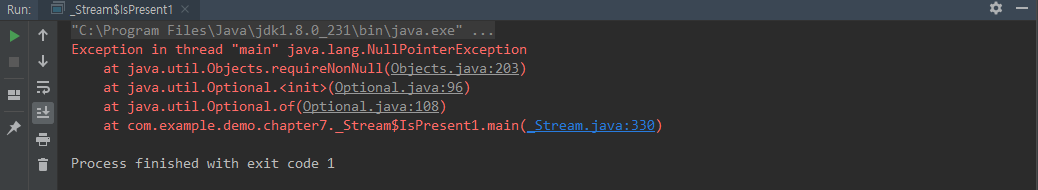
ofNullable()
Optional 객체를 생성하는 메소드
인자가 null 이여도 NullPointerException 은 발생하지 않는다.
ofNullable().get() 할 경우에는 NoSuch....Exception을 발생시킨다
class IsPresent2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional.ofNullable(null)
.ifPresent(val -> System.out.println(val));
}
}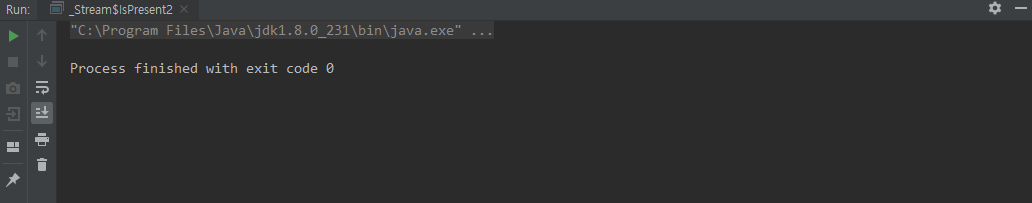
filter()
함수형 인터페이스 Predicate 를 인자로 받고 요소를 추출 할 때 사용한다
class OptionalFilter {
/** Animal 클래스 */
private static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private String getName() {
return name;
}
}
/** 메인 메소드 */
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional<String> name = Optional.ofNullable(new Animal("사자", 5))
.filter(o -> o.age < 10) // 나이가 10 이하 추출
.map(Animal::getName); // 요소의 Getter 메소드 사용
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name.get());
}
}
map()
함수형 인터페이스 Function 을 인자로 받고, 요소를 가공할 때 사용
class OptionalMap {
/** Animal 클래스 */
private static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Gender gender;
public Animal(String name, Integer age, Gender gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Gender getGender() {
return gender;
}
}
/** Gender 클래스 */
enum Gender {
MALE, FEMALE
;
}
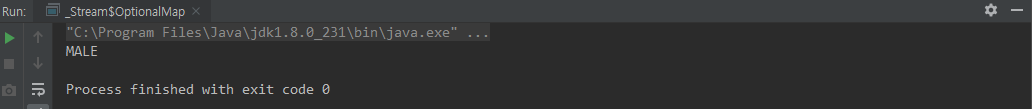
/** 메인 메소드 */
public static void main(String[] args) {
String reuslt = Optional.ofNullable(new Animal(null, 5, Gender.MALE))
.map(Animal::getGender)
.map(Gender::name)
.orElse("Empty");
System.out.println(reuslt);
}
}
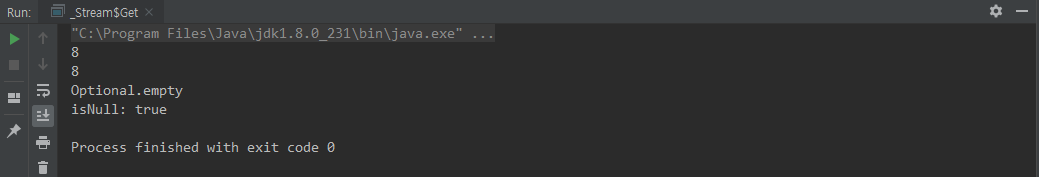
get()
class Get {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = Optional.of(8).get();
System.out.println(value);
String str = Optional.of("8").get();
System.out.println(str);
Object nullVal = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(nullVal);
System.out.println("isNull: " + Optional.empty().equals(nullVal));
}
}
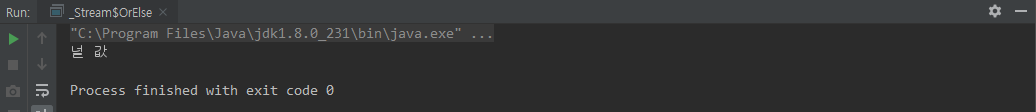
orElse()
class OrElse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object result = Optional.ofNullable(null)
.map(o -> o + "★★★★★")
.orElse("널 값");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
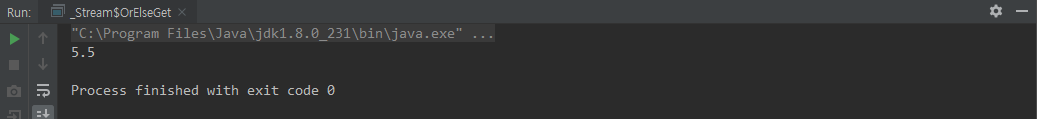
orElseGet()
class OrElseGet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object result = Optional.ofNullable(null)
.map(o -> o + "★★★★★")
.orElseGet(() -> "" + IntStream.of(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10).average().getAsDouble());
System.out.println(result);
}
}
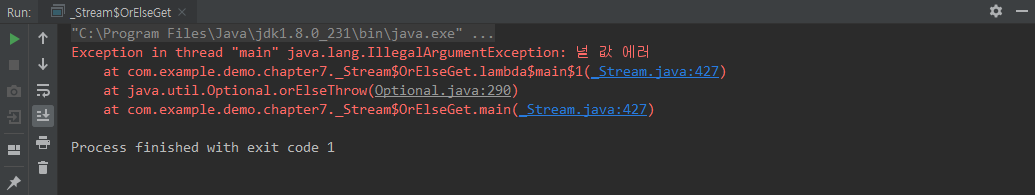
orThrow()
class OrElseThrow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object result = Optional.ofNullable(null)
.map(o -> o + "★★★★★")
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("널 값 에러"));
System.out.println(result);
}
}
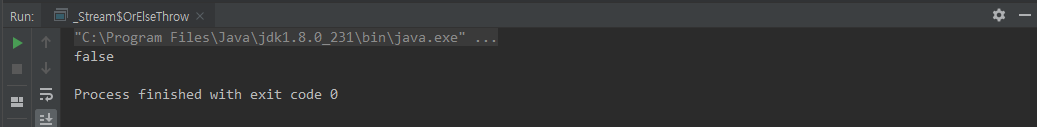
isPresent()
class IsPresent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean result = Optional.ofNullable(null).isPresent();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
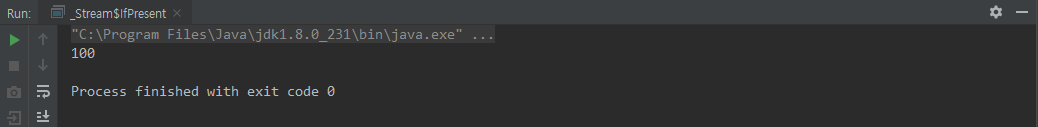
ifPresent()
class IfPresent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional.ofNullable(100).ifPresent(System.out::println);
}
}
# 함수형 인터페이스 생성
함수형 인터페이스는 인터페이스에서 메소드 구현이 가능하다
[Account 클래스]
public class Account {
private String name;
private String email;
private String phoneNumber;
private Integer age;
private Account(String name, String email, String phoneNumber, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber;
this.age = age;
}
public static Account of (String name, String email, String phoneNumber, Integer age) {
return new Account(name,email,phoneNumber,age);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public String getPhoneNumber() {
return phoneNumber;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
}
[CustomValidator 인터페이스]
public interface CustomValidator extends Function<Account, CustomValidator.ValidationResult> {
static CustomValidator isEmailValid () {
return account -> account.getEmail().contains("@") ?
ValidationResult.SUCCESS : ValidationResult.EMAIL_NOT_VALID;
}
static CustomValidator isPhoneNumberValid () {
return account -> account.getEmail().startsWith("0") ?
ValidationResult.SUCCESS : ValidationResult.PHONE_NUMBER_NOT_VALID;
}
static CustomValidator isAgeValid () {
return account -> account.getAge() > 19 ?
ValidationResult.SUCCESS : ValidationResult.IS_NOT_AN_ADULT;
}
default CustomValidator and (CustomValidator other) {
return account -> {
ValidationResult validate = this.apply(account);
return validate.equals(ValidationResult.SUCCESS) ? other.apply(account) : validate;
};
}
enum ValidationResult {
SUCCESS,
PHONE_NUMBER_NOT_VALID,
EMAIL_NOT_VALID,
IS_NOT_AN_ADULT
}
}
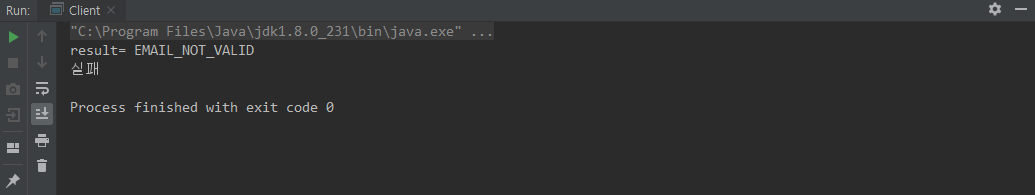
[Client 클래스]
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = Account.of(
"martin",
"test#gmail.com",
"010-1111-1111",
16
);
ValidationResult result = isEmailValid()
.and(CustomValidator.isAgeValid())
.and(CustomValidator.isAgeValid())
.and(CustomValidator.isAgeValid())
.apply(account);
System.out.println("result= " + result);
if (result != ValidationResult.SUCCESS) {
System.out.println("실패");
} else {
System.out.println("성공");
}
}
}
[결과]
[null-safety]
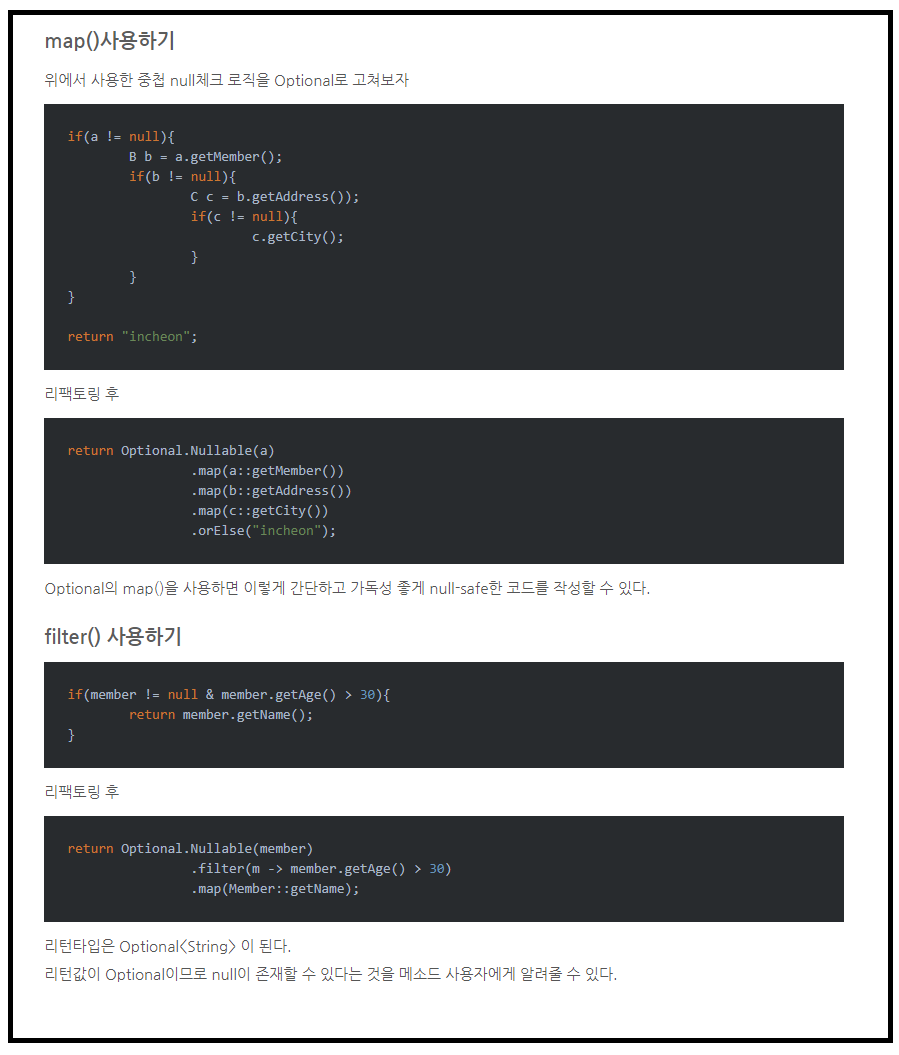
# Stream 메소드
[ ] : 생략가능
obj : 오브젝트 타입
int : 인트 타입
double : 더블 타입
long : 롱 타입
n : 숫자
stream : 스트림 클래스
| 작업 | 메소드 | 설명 |
| 스트림 생성 (Create Operations) |
Arrays.stream() | Array 타입 |
| Collections.stream() | Collection 타입 | |
| Stream.empty() | 빈 값 ( [] ) | |
| Stream.builder().add(obj).build() | 추가 | |
| Stream.generate(Supplier).limit(n) | 무한반복 추가 | |
| Stream.iterate(n1, n2 -> n2).limit(n) | 무한반복 추가 | |
| IntStream.range(n1, n2) | >=n1, <n2 | |
| IntStream.rangeClosed(n1, n2) | >=n1, <=n2 | |
| new Random().ints(n) | 랜덤 숫자 생성 | |
| 중간 연산자 (Intermediate Operations) |
.limit(n) | ~n 요소 까지 |
| .filter(Predicate) | 추출 | |
| .map(Function) | 가공 | |
| .flatMap(Function) | 중첩제거 가공 | |
| .sorted( [Comparator] ) | 정렬 | |
| .distinict() | 중복제거 | |
| .peek(Consumer) | 특정값 출력용 | |
| .skip(n) | 건너뛰기 | |
| Stream.concat(stream1, stream2) | 연결하기 | |
| .reduce(Bifunction) | 줄이기 | |
| IntStream.boxed() | Stream 변환 | |
| Stream.mapToInt | IntStream 변환 | |
| 최종 연산자 (Terminal Operations) |
IntStream.count() | 총 개수 |
| .sum() | 총 합 | |
| .min() | 최소값 | |
| .max() | 최대값 | |
| .average() | 평균 | |
| .forEach( consumer) | for each 문 | |
| .collect(Collectors.toList()) | List 타입 반환 | |
| .collect(Collectors.toSet()) | Set 타입 반환 | |
| .collect(Collectors.toMap()) | Map 타입 반환 | |
| .collect(Collectors.joining( [delimiter], [prefix], [suffix] )) | 조인 | |
| .collect(Collectors.groupingBy( action )) | 자료형 그룹화 | |
| .collect(Collectors.partitioningBy( action )) | Boolean 그룹화 | |
| .collect(Collectors.averageingInt(obj -> int)) | int 평균 | |
| .collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(obj -> double)) | double 평균 | |
| .collect(Collectors.averagingLong(obj -> long )) | long 평균 | |
| .collect(Collectors.summingInt( action )) | int 누적합계 | |
| .collect(Collectors.summingDouble( action )) | double 누적합계 | |
| .collect(Collectors.summingLong( action )) | long 누적합계 | |
| .collect(Collectors.summarizingInt( action )) | count ~ average | |
| .collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble( action )) | count ~ average | |
| .collect(Collectors.summarizingLong( action )) | count ~ average | |
| .anyMatch(Predicate) | 1개 일치 | |
| .allMatch(Predicate) | 모두 일치 | |
| .noneMatch(Predicate) | 모두 불일치 |
# 스트림 생성 (Create Operations)
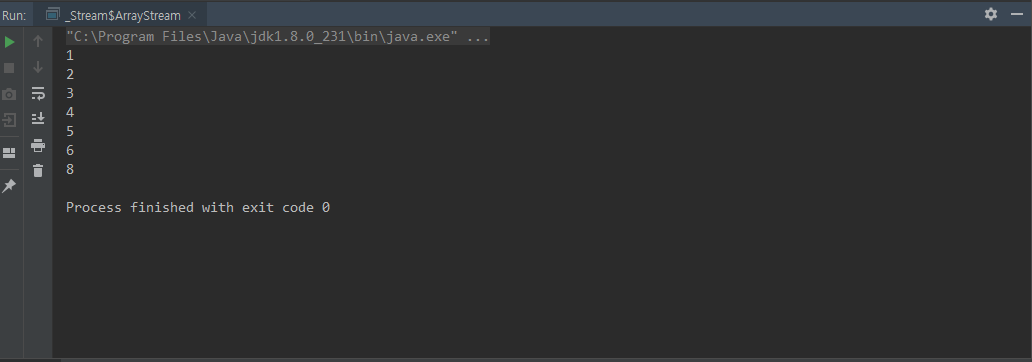
Arrays.stream()
배열으로 Stream
class ArrayStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1,2,3,4,5,6,8};
Arrays.stream(numbers)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
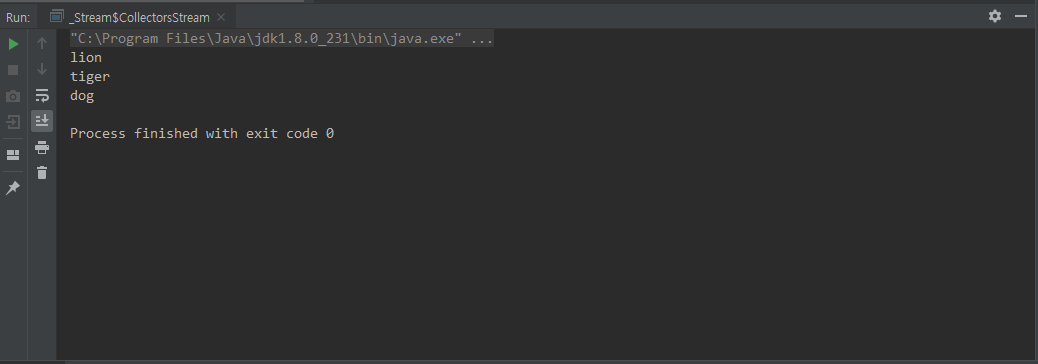
Collectors.stream()
Collection 의 list, set, map 으로 Stream 생성
class CollectorsStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Arrays.asList("lion", "tiger", "dog")
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
Stream.empty()
빈 값의 Stream 생성 null 대신 사용하는 빈 값, list 일 때 [] 와 같다
class EmptyStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.empty()
.forEach(System.out::println); // []
}
}
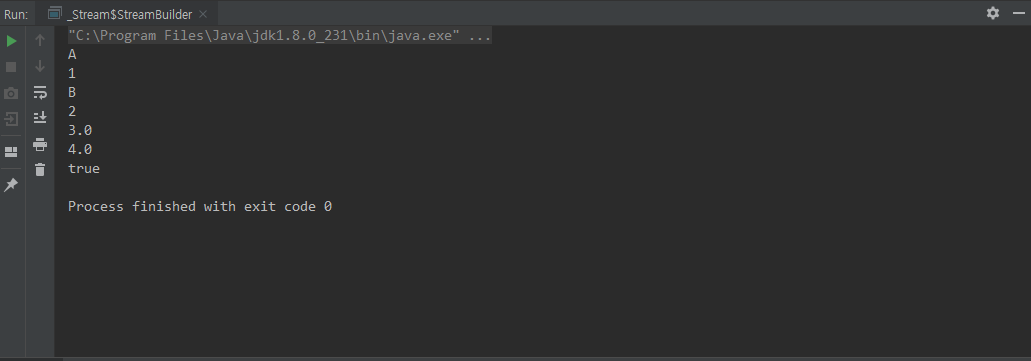
Stream.builder()
빌더패턴을 이용한 Stream 생성
class StreamBuilder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.builder()
.add("A")
.add(1)
.add('B')
.add(2L)
.add(3.0f)
.add(4.0)
.add(true)
.build()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
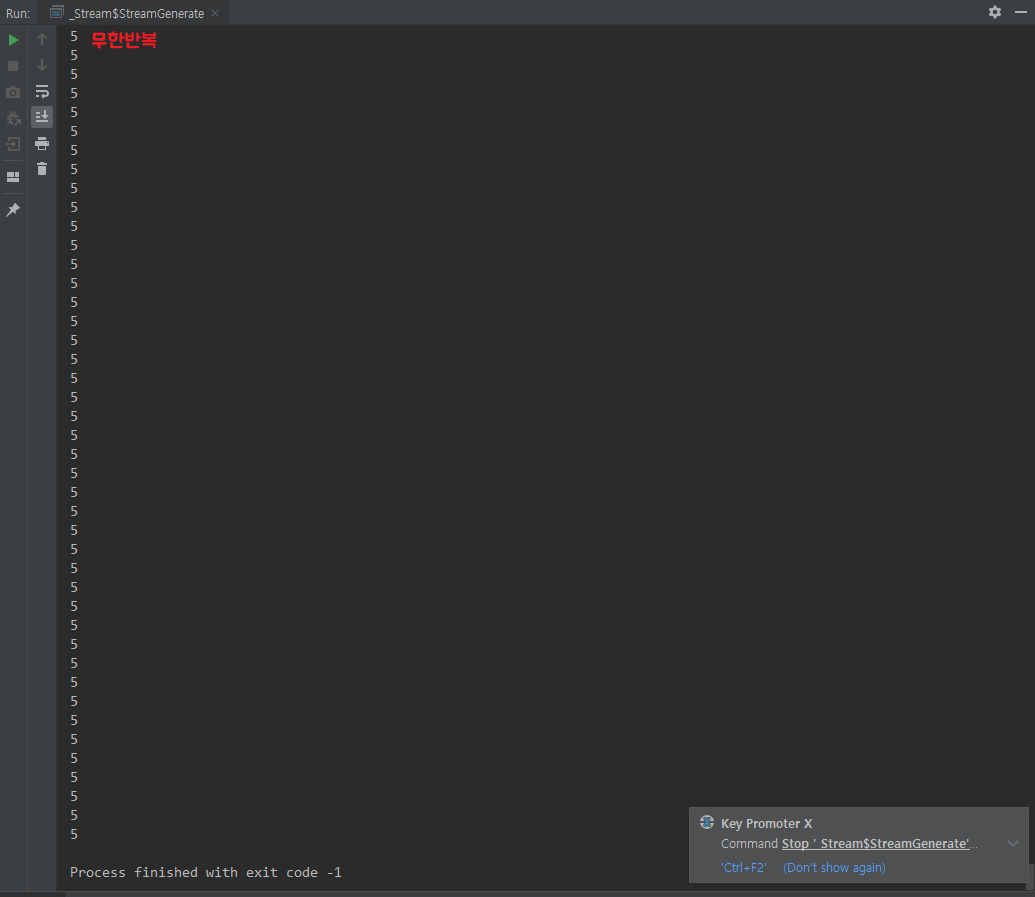
Stream.generate(Supplier)
함수형 인터페이스 Supplier 를 이용하여 Stream 생성 .limit(n) 이 없는 경우 무한 반복한다
class StreamGenerate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.generate(() -> 5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
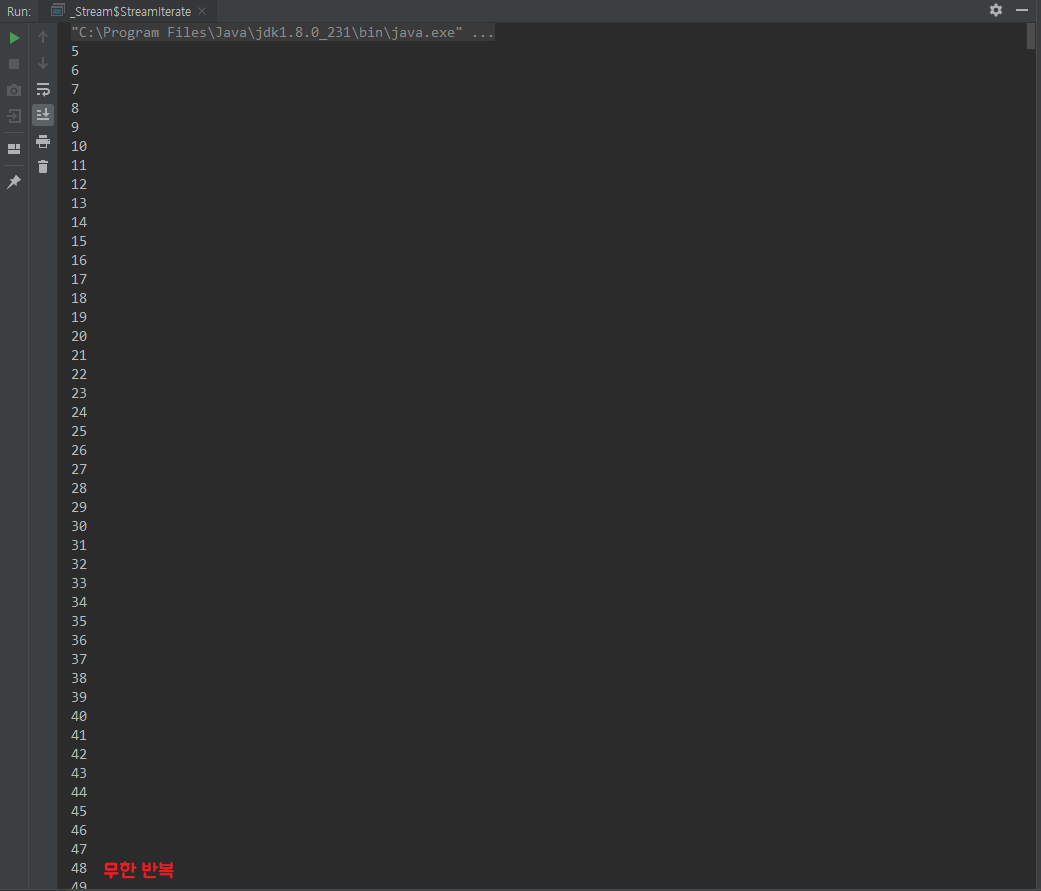
Stream.iterate()
함수형 인터페이스 Function 을 상속한 UnaryOperator 를 이용한 Stream 생성
첫 번째 인자는 초기값이고, 두 번째 인자는 Function 이라고 보면 된다
class StreamIterate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.iterate(5,integer -> integer+1)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
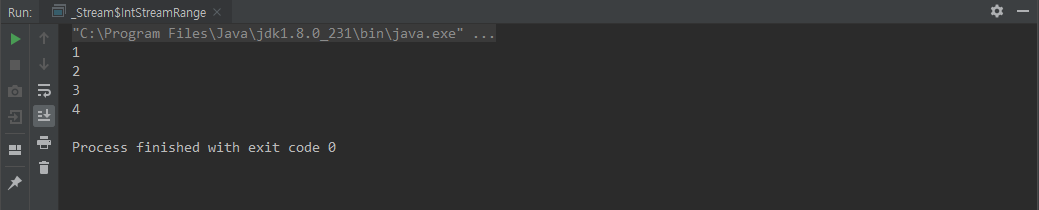
IntStream.range()
range() 는 IntStream 과 LongStream 에서만 사용한다
IntStream 은 int 타입으로만 이루어져있다.
range(n1, n2) 일 때 인자들의 타입은 모두 int 이며, 생성되는 Stream은 n1 이상 n2 미만 이다
(LongStream 은 long 타입으로 이루어져있고, 인자들의 타입은 long 이다)
class IntStreamRange {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntStream.range(1, 5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
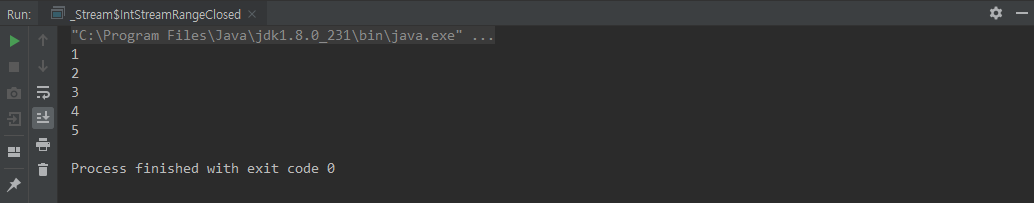
IntStream.rangeClosed()
rangeClosed() 는 IntStream 과 LongStream 에서만 사용한다
IntStream 은 int 타입으로만 이루어져있다.
range(n1, n2) 일 때 인자들의 타입은 모두 int 이며, 생성되는 Stream은 n1 이상 n2 이하 이다
(LongStream 은 long 타입으로 이루어져있고, 인자들의 타입은 long 이다)
class IntStreamRangeClosed {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 5)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
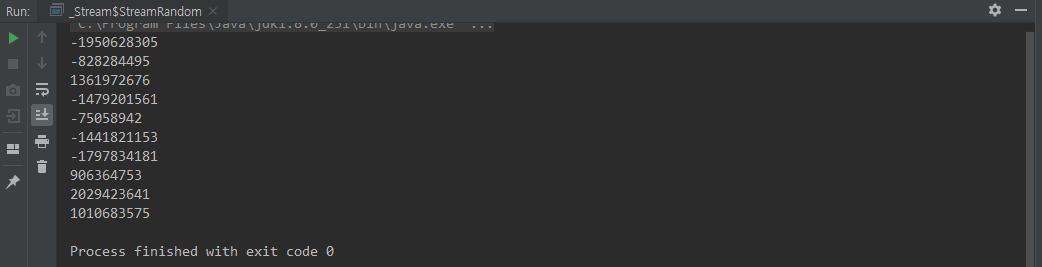
new Random().ints()
Random 인스턴스에서 Stream 을 생성할 수 있다
.ints() 는 IntStream 으로 생성, .longs() 는 LongStream, .doubles() 는 DoubleStream 으로 생성된다
.ints(n) 에서 n 은 n 개의 랜덤 int 타입 숫자를 생성한다
class StreamRandom {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Random().ints(10)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
# 중간 연산자 (Intermediate Operations)
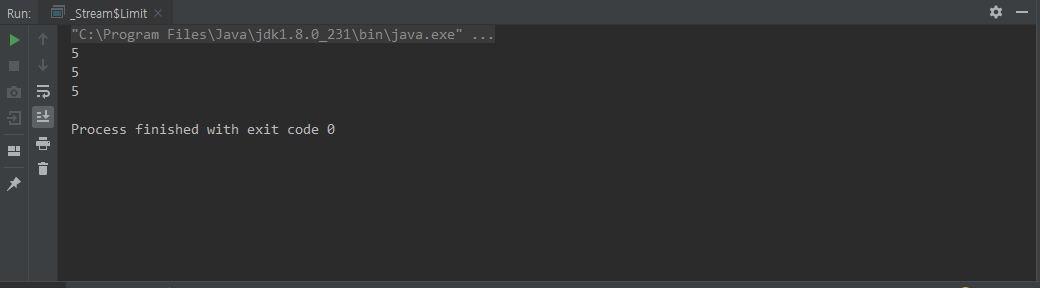
limit()
limit(n) 은 n 개의 요소만 사용한다는 뜻이다.
아래코드는 무한개의 요소 중 3개의 요소만 사용하는 것이다
class Limit {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.generate(() -> 5)
.limit(3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
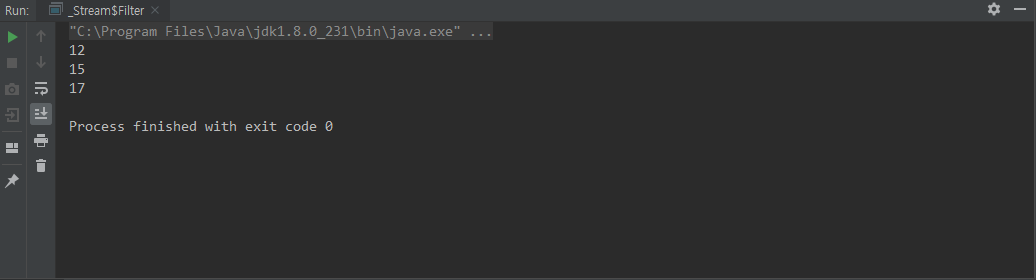
filter()
원하는 요소만 추출하기 위한 메소드이다.
인자로는 Predicate를 받는데, boolean값을 반환하는 람다식을 넣으면 된다.
class Filter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of(1,5,7,9,12,15,17)
.filter(n -> n>10)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
map()
스트림 내 요소를 가공한다.
인자로는 Function을 받는다
class Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 100 단위 절삭
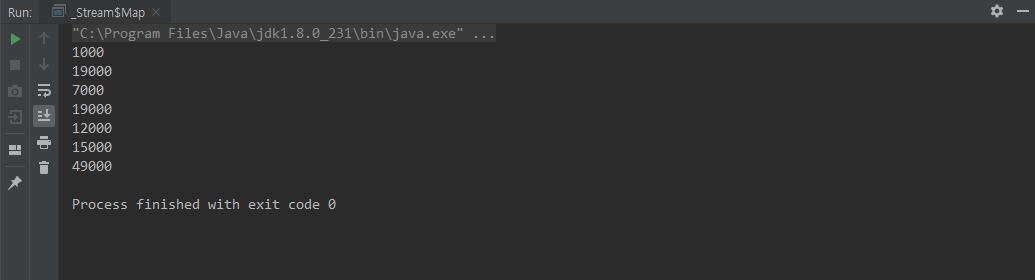
Stream.of(1150,19310,7400,19900,12100,15590,49990)
.map(n -> (int) Math.floor(n/1000) * 1000)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
mapToInt()
Stream 에서 IntStream 으로 바꾼다
Stream 에서는 .sum(), .average() 등 을 사용할 수 없기 때문이다
(mapToLong() 과 mapToDoubles() 가 있다)
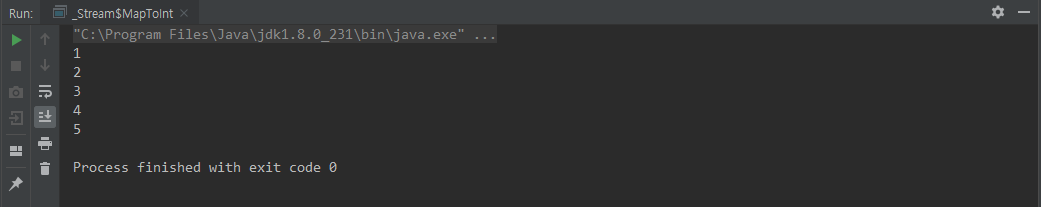
class MapToInt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("1","2","3","4","5") // Stream
.mapToInt(Integer::parseInt) // IntStream
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
flatMap(Function)
중첩 구조를 한 단계 제거하고 단일 컬렉션으로 만들어 주는 역할을 한다. 이러한 작업을 flattening이라고 한다.
= 이중 for 문
class LdFlatMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] arr = {
{"minus one", "zero", "one"},
{"two", "Three"},
{"Four", "Five", "Six"},
{"eight", "ten"}
};
Stream.of(arr)
.flatMap(Stream::of)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
sorted()
요소들을 정렬 할 때 사용한다 - 오름차순
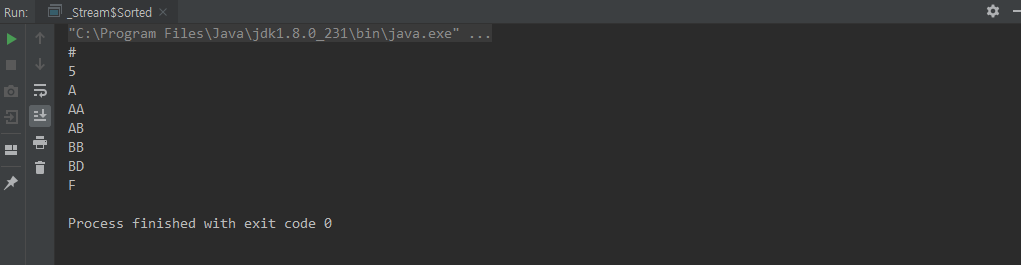
class Sorted {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("BD", "AB", "AA", "BB", "#", "5", "A","F")
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder()
요소들을 정렬 할 때 사용한다 - 내림차순
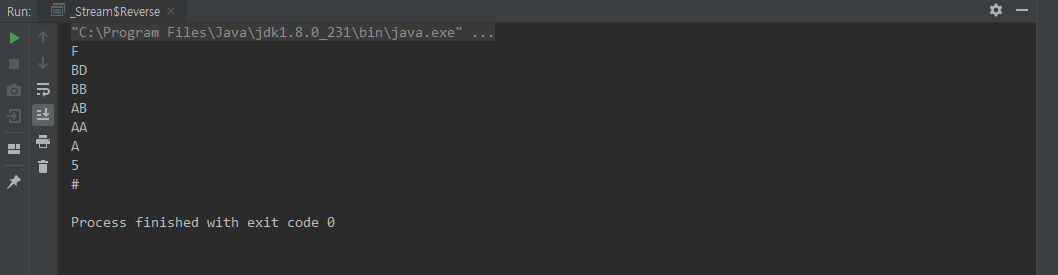
class Reverse {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("BD", "AB", "AA", "BB", "#", "5", "A","F")
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
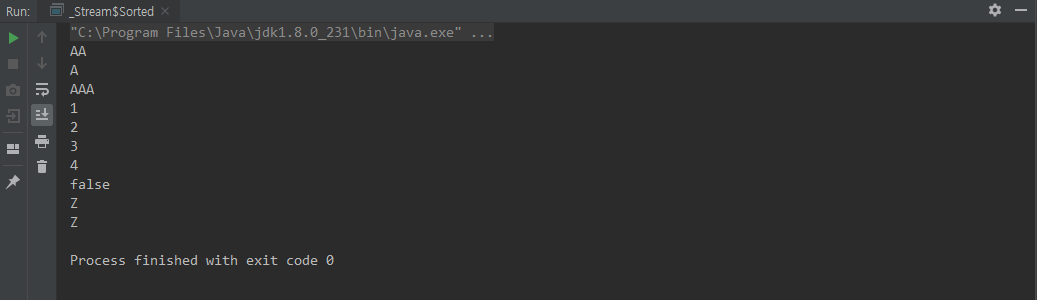
distinict()
중복된 요소들은 제거된다
아래 코드에서 'Z' 는 Char 타입, "Z" 는 String 이기 때문에 제거가 안된 것 이다
class Distinct {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("AA","AA","A","AAA",1,1,2,3,4,false,false,'Z',"Z")
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
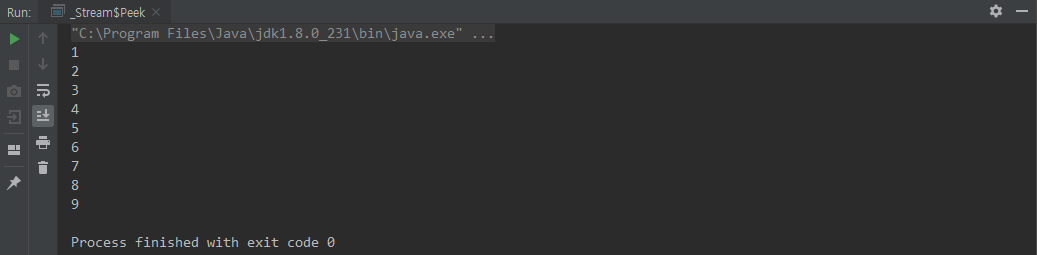
peek(Consumer)
함수형 인터페이스 Consumer 를 이용한다.
각 요소에 특정한 연산을 수행하는 메소드이다. '살짝 들여다본다'라는 단어로 중간에 값을 출력해볼 때 이용할 수 있다.
forEach() 와 다른점은 peek() 은 중간 연산자이고, forEach() 는 최종 연산자이다
class Peek {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
.peek(System.out::println)
.mapToInt(value -> value)
.toArray();
}
}
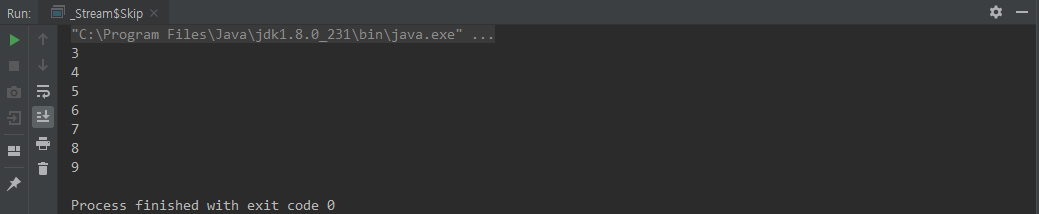
skip()
skip(n) 은 n만큼 요소를 건너뛴다.
class Skip {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
.skip(2)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
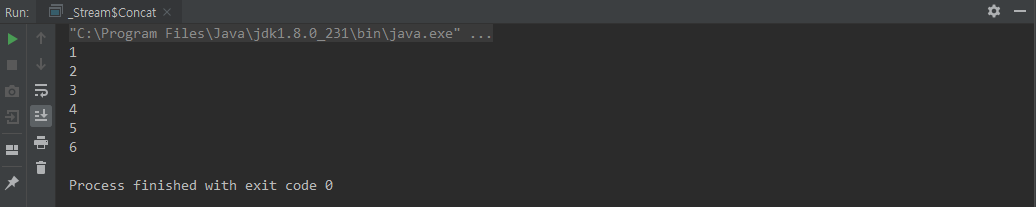
Stream.concat()
class Concat {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.concat(
Stream.of(1,2,3),
Stream.of(4,5,6)
)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
reduce()
코드를 줄일 때 사용한다
인자 1개 = BinaryOperator
- 반환 타입 : Optional<Stream 요소의 타입>
인자 2개 = T , BinaryOperator
- 반환 타입 : 첫 번째 인자와 같은 타입
인자 3개 = U, BiFunction, BinaryOPerator
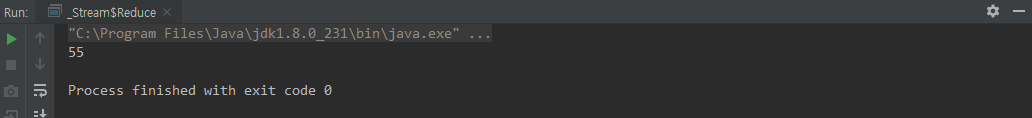
class Reduce {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인자 1개
Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 , 10) // Stream
.reduce((total, currentValue) -> total + currentValue) // Optional<Integer>
.ifPresent(System.out::println);
}
}
초기값을 줄 수 있으며 리턴타입은 초기값과 같은 타입으로 리턴된다
(위에서는 Optional<Integer> 였지만 아래는 int 타입으로 반환)
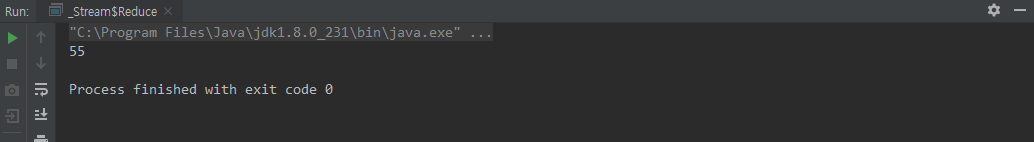
class Reduce2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 인자 2개
int result = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 , 10)
.reduce(100, (total, currentValue) -> total + currentValue);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
# 최종 연산자 (Terminal Operations)
count()
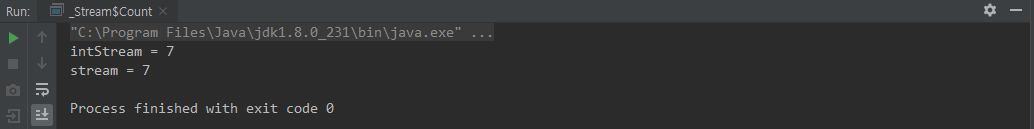
class Count {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50,60,70).count();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
Long stream = Stream.of(10,20,30,40,50,60,70).count();
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
}
}
sum()
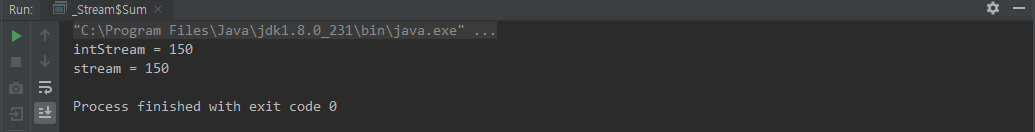
class Sum {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50).sum();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
int stream = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.mapToInt(Animal::getAge)
.sum();
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
}
}
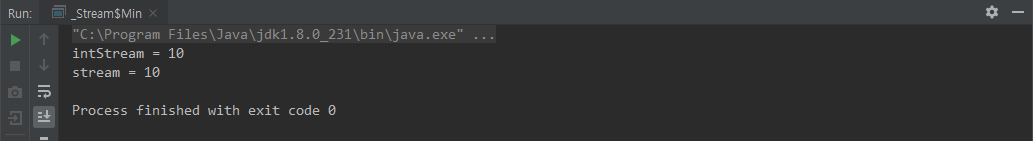
min()
class Min {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50).min().getAsInt();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
int stream = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.mapToInt(Animal::getAge)
.min()
.getAsInt();
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
}
}
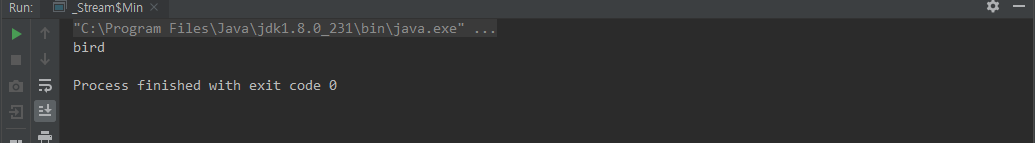
min(Comparator)
class Min {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.min(Comparator.comparing(o -> o.name)) // Optional<String>
.ifPresent(animal -> System.out.println(animal.name));
}
}
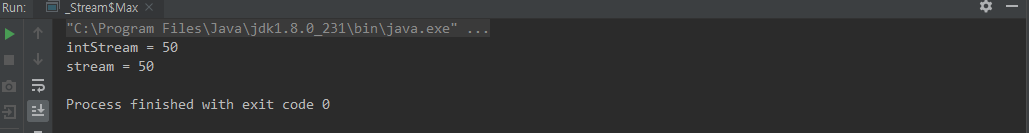
max()
class Max {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50).max().getAsInt();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
int stream = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.mapToInt(Animal::getAge)
.max()
.getAsInt();
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
}
}
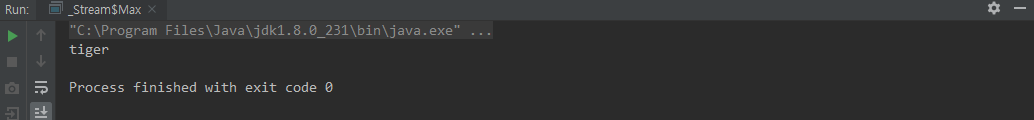
max(Comparator)
class Max {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.max(Comparator.comparing(o -> o.name)) // Optional<String>
.ifPresent(animal -> System.out.println(animal.name));
}
}
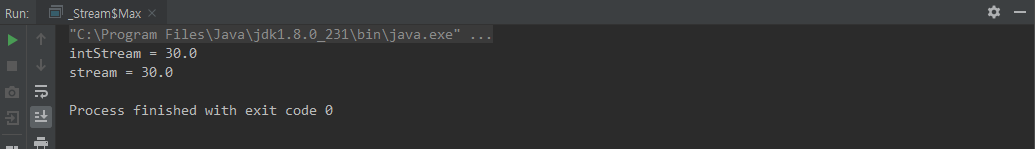
average()
class Average {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50)
.average() // OptionalDouble
.getAsDouble();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
double stream = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
)
.mapToInt(Animal::getAge)
.average()
.getAsDouble();
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
}
}
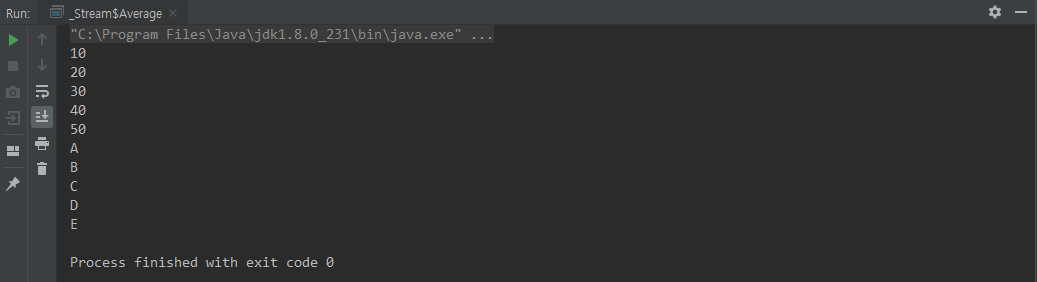
forEach()
class ForEach {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50)
.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.of("A","B","C","D","E")
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
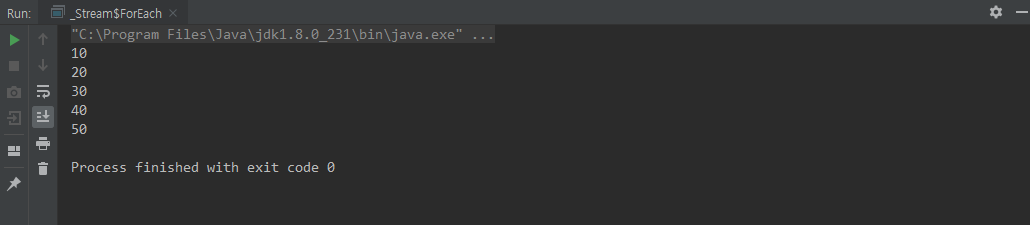
toArray()
int 타입 배열을 리턴한다
class ToArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ints = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50).toArray();
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.println(anInt);
}
}
}
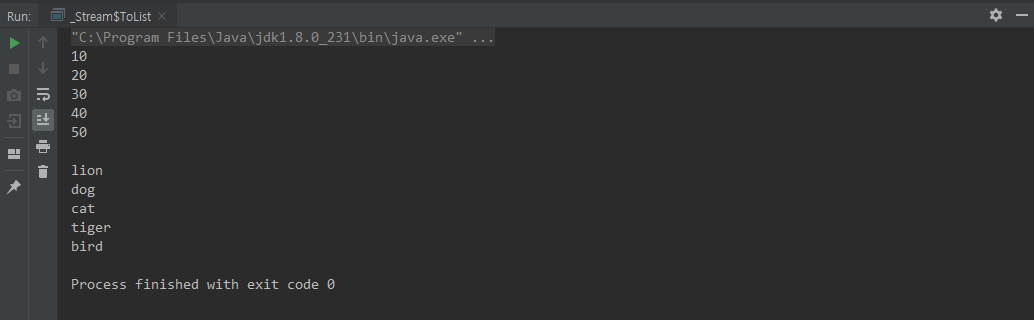
collect(Collectors.toList())
class ToList {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Integer integer : intStream) {
System.out.println(integer);
}
System.out.println();
List<Animal> animals = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Animal animal : animals) {
System.out.println(animal.name);
}
}
}
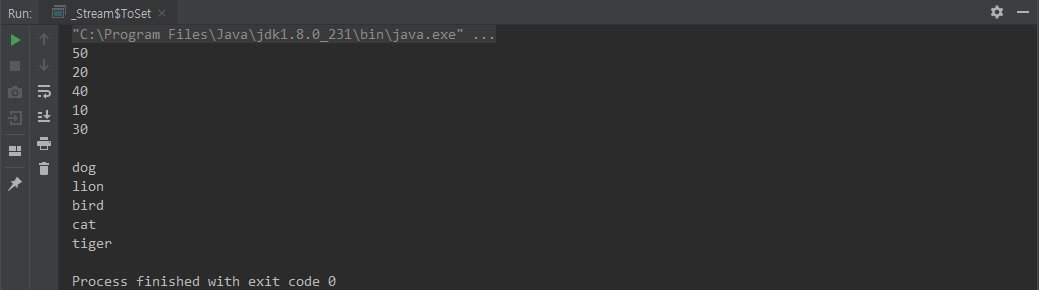
collect(Collectors.toSet())
class ToSet {
static class Animal {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
private Animal(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> intStream = IntStream.of(10,20,30,40,50)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
intStream.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
Set<Animal> animals = Stream.of(
new Animal("lion", 10),
new Animal("dog", 20),
new Animal("cat", 30),
new Animal("tiger", 40),
new Animal("bird", 50)
).collect(Collectors.toSet());
animals.forEach(animal -> System.out.println(animal.name));
}
}
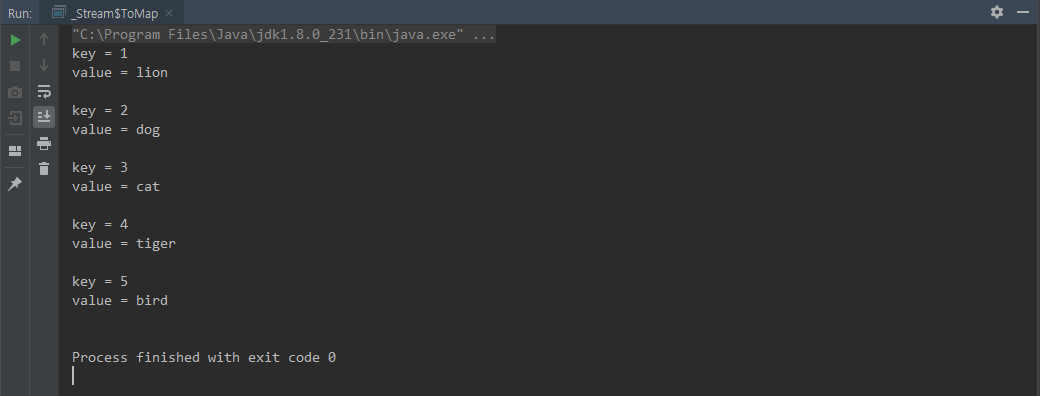
collect(Collectors.toMap())
class ToMap {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Long, String> animals = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
).collect(Collectors.toMap(o -> o.id, o -> o.name));
for (Long key : animals.keySet()) {
System.out.println("key = " + key);
System.out.println("value = " + animals.get(key));
System.out.println();
}
}
}
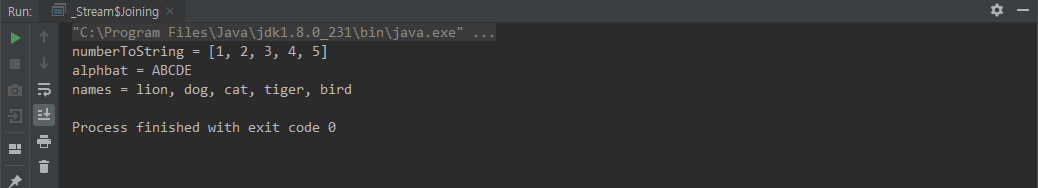
collect(Collectors.joining( [구분자], [맨 앞], [맨 뒤] )))
class Joining {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String numberToString = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.map(String::valueOf)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", ", "[", "]"));
System.out.println("numberToString = " + numberToString);
String alphabat = Stream.of("A", "B", "C", "D", "E")
.collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println("alphbat = " + alphabat);
String names = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.map(animal -> animal.name)
.collect(Collectors.joining(", "));
System.out.println("names = " + names);
}
}
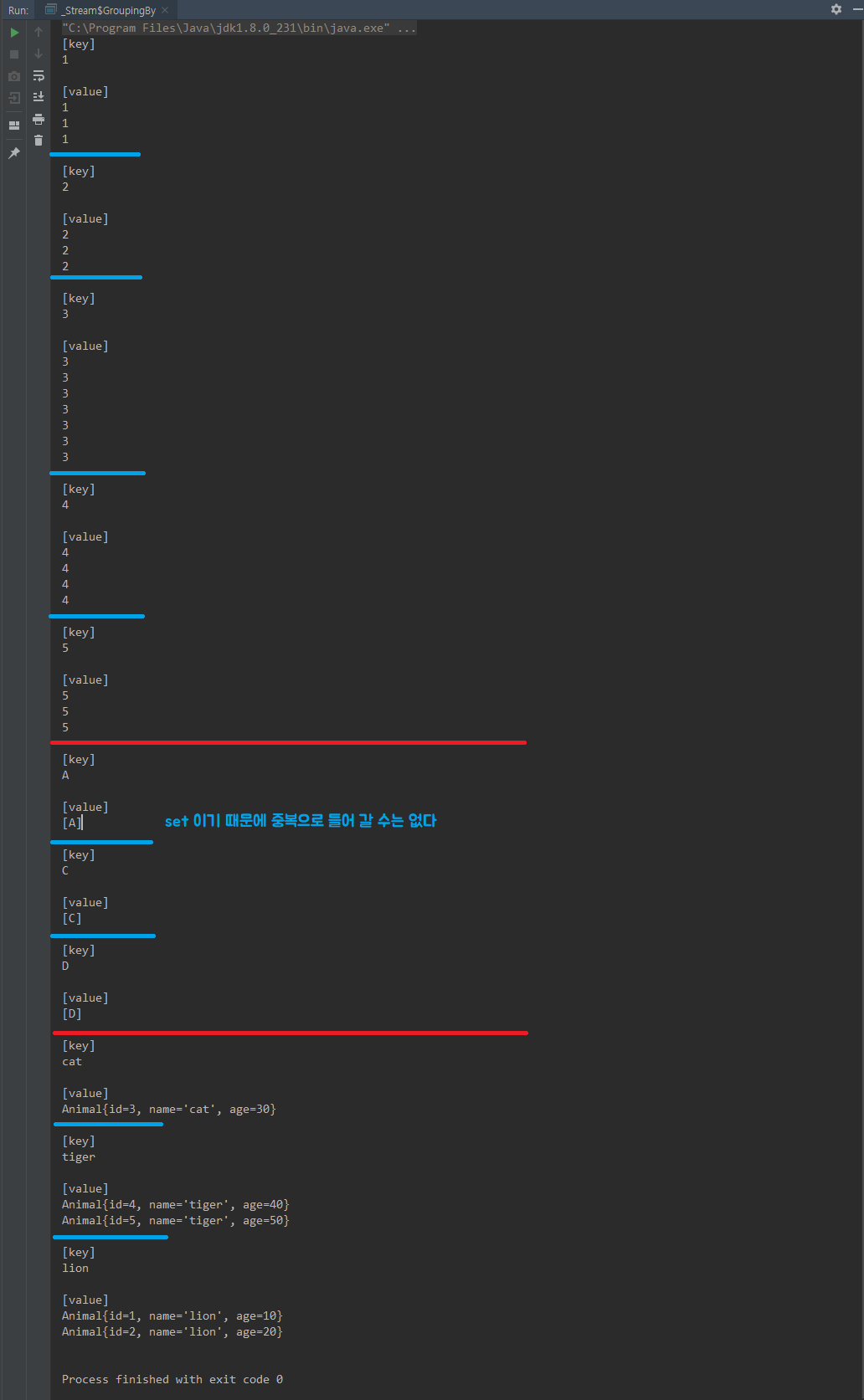
collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function))
Function 함수형 인터페이스를 인자로 한다
기본 결과 값으로는 Map<리턴타입, List<요소타입>> 으로 리턴 된다.
(Function 에서 리턴된 타입을 Map 의 Key 로 설정한다.)
class GroupingBy {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Collectors.groupingBy(classifier)
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> ints = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,1,2,3,4,5,3,4,5,4,3,3,3)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Integer::intValue));
ints.forEach((key, values) -> {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
values.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
});
// Collectors.groupingBy(classifier, downStream)
Map<String, Set<String>> alphabat = Stream.of("A", "A", "C", "D", "D")
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(o -> o, Collectors.toSet()));
alphabat.forEach((key, values) -> {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
values.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
});
// Collectors.groupingBy(classifier)
Map<String, List<Animal>> animals =Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Animal::getName));
for (String key : animals.keySet()) {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
for (Animal animal : animals.get(key)) {
System.out.println(animal);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
[ Collectors.groupingBy(classifier, mapFactory, downStream) 는 아래 사이트 참고 바람 ]
[Java8] sorted groupBy
이번에는 간단한 주제로 글을 짧게 남겨보고자 한다. stream의 groupBy와 관련된 내용이다. 개발을 하다가 List에 있는 객체의 특정 값으로 groupBy를 했다. 문제는 groupBy된 결과가 group key로 사용한 값��
devidea.tistory.com
collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(Predicate))
Predicate 함수형 인터페이스를 인자로 한다
조건에 일치 true 일 경우 true 그룹에 속하게 되며, 조건에 일치하지 않으면 false 그룹에 속한다
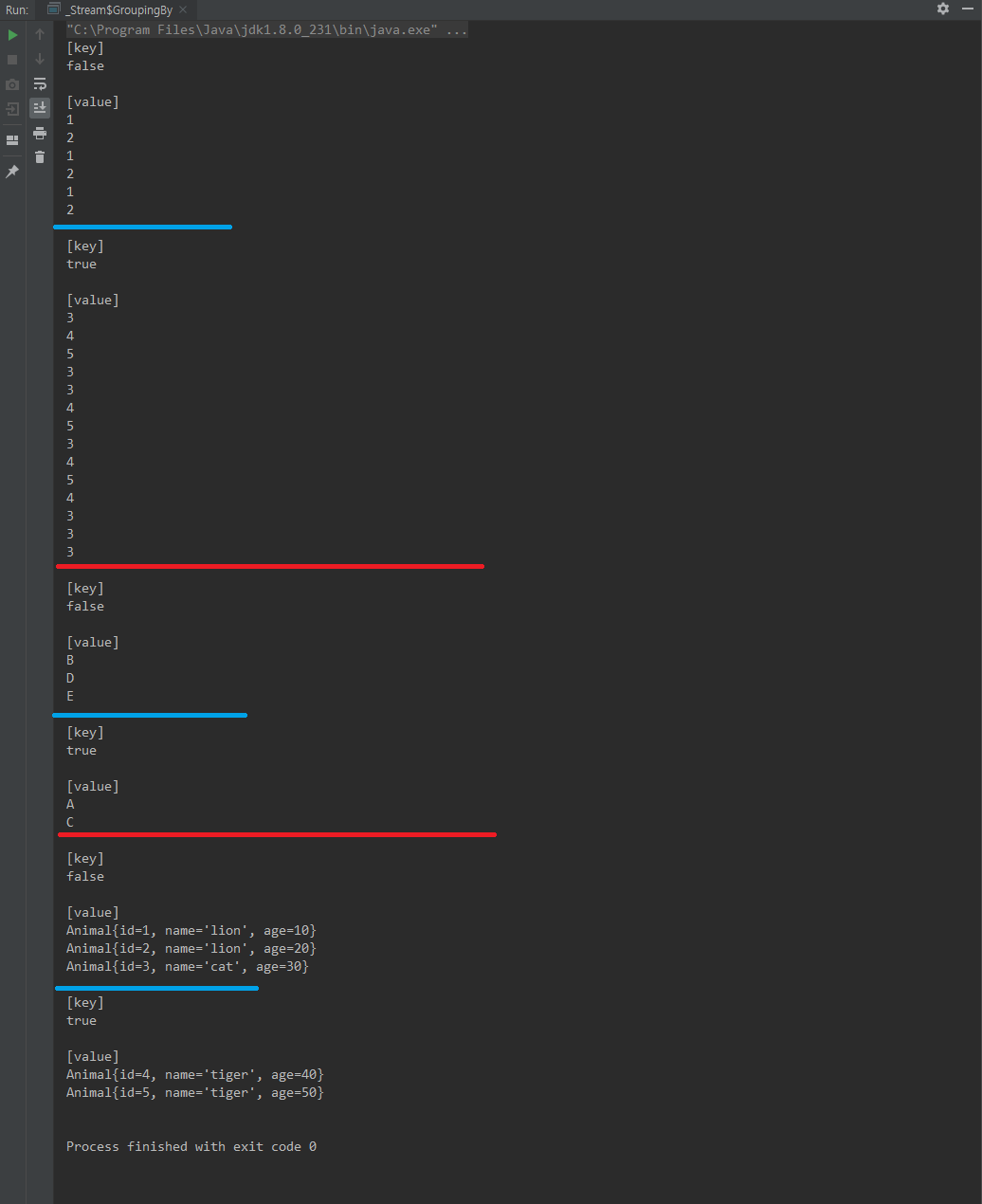
class GroupingBy {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Collectors.partitioningBy(predicate)
Map<Boolean, List<Integer>> ints = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5,1,2,3,1,2,3,4,5,3,4,5,4,3,3,3)
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(i -> i > 2));
ints.forEach((key, values) -> {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
values.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
});
// Collectors.partitioningBy(predicate, downStream)
Map<Boolean, Set<String>> alphabat = Stream.of("A", "B", "C", "D", "E")
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(str -> str.equals("A") || str.equals("C"), Collectors.toSet()));
alphabat.forEach((key, values) -> {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
values.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
});
// Collectors.partitioningBy(predicate)
Map<Boolean, List<Animal>> animals = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
)
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(animal -> animal.age>30));
for (Boolean key : animals.keySet()) {
System.out.println("[key]");
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[value]");
for (Animal animal : animals.get(key)) {
System.out.println(animal);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
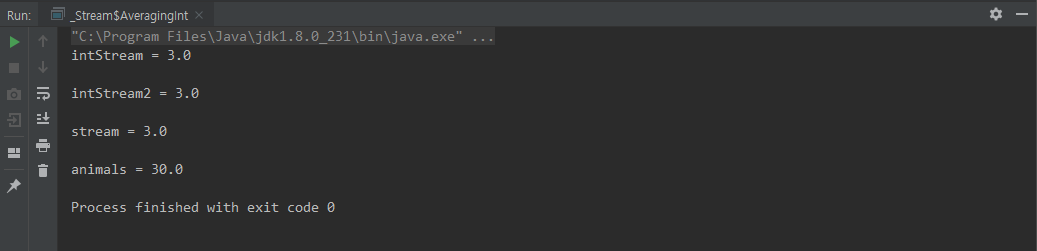
collect(Collectors.averageingInt(ToIntFunction))
class AveragingInt {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream Collectors.averagingInt
Double intStream = IntStream.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Integer::intValue));
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
System.out.println();
// IntStream average
Double intStream2 = IntStream.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.average().getAsDouble();
System.out.println("intStream2 = " + intStream2);
System.out.println();
// Stream Collectors.averagingInt
Double stream = Stream.of("1","2","3","4","5")
.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
System.out.println();
// Collectors.averagingInt
Double animals = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
)
.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Animal::getAge));
System.out.println("animals = " + animals);
}
}
collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(obj -> double))
averagingInt 와 비슷한 방식
collect(Collectors.averagingLong(obj -> long ))
averagingInt 와 비슷한 방식
collect(Collectors.summingInt( action ))
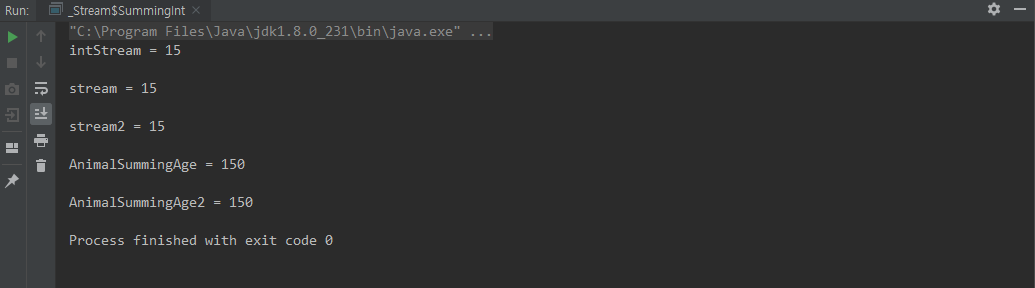
class SummingInt {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream Collectors.summingInt
Integer intStream = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.sum();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
System.out.println();
// Stream Collectors.summingInt
Integer stream = Stream.of("1","2","3","4","5")
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
System.out.println();
// Stream Collectors.summingInt
Integer stream2 = Stream.of("1", "2", "3", "4", "5")
.mapToInt(Integer::parseInt)
.sum();
System.out.println("stream2 = " + stream2);
System.out.println();
// Collectors.summingInt
Integer AnimalSummingAge = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
)
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Animal::getAge));
System.out.println("AnimalSummingAge = " + AnimalSummingAge);
System.out.println();
// Collectors.summingInt 2
Integer AnimalSummingAge2 = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
).mapToInt(Animal::getAge).sum();
System.out.println("AnimalSummingAge2 = " + AnimalSummingAge2);
}
}
collect(Collectors.summingDouble( action ))
summingInt 와 비슷한 방식
collect(Collectors.summingLong( action ))
summingInt 와 비슷한 방식
collect(Collectors.summarizingInt( action ))
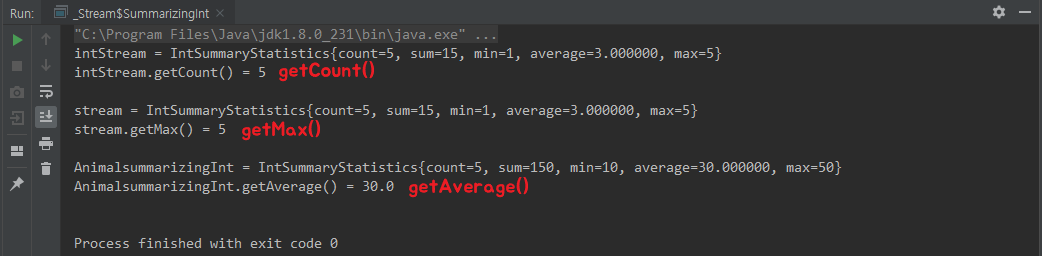
class SummarizingInt {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream Collectors.SummarizingInt
IntSummaryStatistics intStream = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("intStream = " + intStream);
System.out.println("intStream.getCount() = " + intStream.getCount());
System.out.println();
// Stream Collectors.SummarizingInt
IntSummaryStatistics stream = Stream.of("1","2","3","4","5")
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Integer::parseInt));
System.out.println("stream = " + stream);
System.out.println("stream.getMax() = " + stream.getMax());
System.out.println();
// Collectors.SummarizingInt
IntSummaryStatistics AnimalsummarizingInt = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "lion", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "tiger", 50)
)
.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Animal::getAge));
System.out.println("AnimalsummarizingInt = " + AnimalsummarizingInt);
System.out.println("AnimalsummarizingInt.getAverage() = " + AnimalsummarizingInt.getAverage());
System.out.println();
}
}
collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble( action ))
summarizingInt 와 비슷한 방식
collect(Collectors.summarizingLong( action ))
summarizingInt 와 비슷한 방식
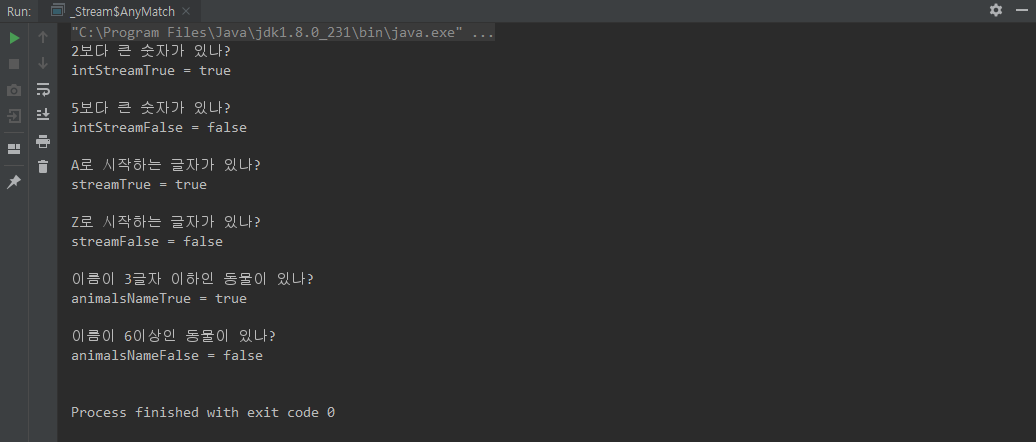
anyMatch(Predicate)
class AnyMatch {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream anyMatch True
boolean intStreamTrue = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.anyMatch(value -> value > 2);
System.out.println("2보다 큰 숫자가 있나?");
System.out.println("intStreamTrue = " + intStreamTrue);
System.out.println();
// IntStream anyMatch False
boolean intStreamFalse = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.anyMatch(value -> value > 5);
System.out.println("5보다 큰 숫자가 있나?");
System.out.println("intStreamFalse = " + intStreamFalse);
System.out.println();
// Stream anyMatch True
boolean streamTrue = Stream.of("AZ","BZ","CZ","DZ","EZ")
.anyMatch(value -> value.startsWith("A"));
System.out.println("A로 시작하는 글자가 있나?");
System.out.println("streamTrue = " + streamTrue);
System.out.println();
// Stream anyMatch False
boolean streamFalse = Stream.of("A","B","C","D","E")
.anyMatch(value -> value.startsWith("Z"));
System.out.println("Z로 시작하는 글자가 있나?");
System.out.println("streamFalse = " + streamFalse);
System.out.println();
// animals anyMactch True
boolean animalsNameTrue = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.anyMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() < 4);
System.out.println("이름이 3글자 이하인 동물이 있나?");
System.out.println("animalsNameTrue = " + animalsNameTrue);
System.out.println();
// animals anyMactch False
boolean animalsNameFalse = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.anyMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() > 5);
System.out.println("이름이 6이상인 동물이 있나?");
System.out.println("animalsNameFalse = " + animalsNameFalse);
System.out.println();
}
}
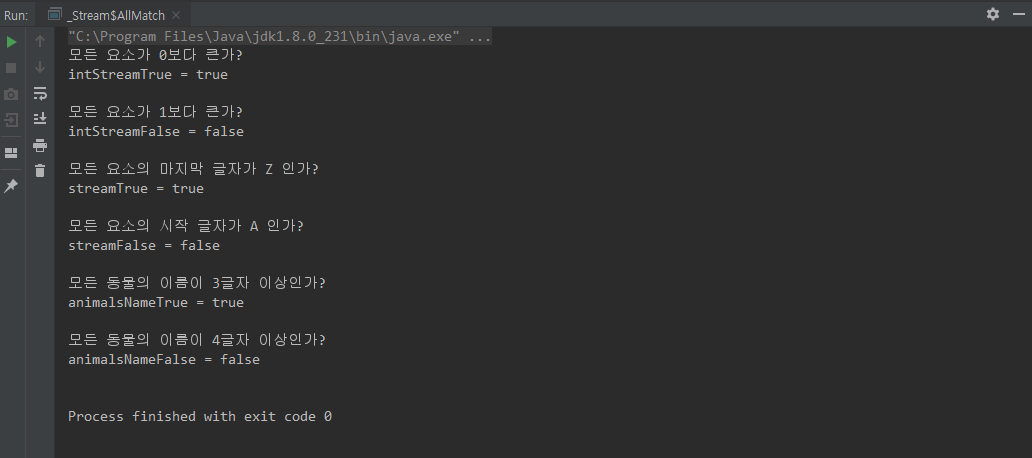
allMatch(Predicate)
class AllMatch {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream allMatch True
boolean intStreamTrue = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.allMatch(value -> value > 0);
System.out.println("모든 요소가 0보다 큰가?");
System.out.println("intStreamTrue = " + intStreamTrue);
System.out.println();
// IntStream allMatch False
boolean intStreamFalse = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.allMatch(value -> value > 1);
System.out.println("모든 요소가 1보다 큰가? ");
System.out.println("intStreamFalse = " + intStreamFalse);
System.out.println();
// Stream allMatch True
boolean streamTrue = Stream.of("AZ","BZ","CZ","DZ","EZ")
.allMatch(value -> value.endsWith("Z"));
System.out.println("모든 요소의 마지막 글자가 Z 인가?");
System.out.println("streamTrue = " + streamTrue);
System.out.println();
// Stream allMatch False
boolean streamFalse = Stream.of("A","B","C","D","E")
.allMatch(value -> value.startsWith("A"));
System.out.println("모든 요소의 시작 글자가 A 인가?");
System.out.println("streamFalse = " + streamFalse);
System.out.println();
// animals allMatch True
boolean animalsNameTrue = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.allMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() > 2);
System.out.println("모든 동물의 이름이 3글자 이상인가?");
System.out.println("animalsNameTrue = " + animalsNameTrue);
System.out.println();
// animals allMatch False
boolean animalsNameFalse = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.allMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() > 3);
System.out.println("모든 동물의 이름이 4글자 이상인가?");
System.out.println("animalsNameFalse = " + animalsNameFalse);
System.out.println();
}
}
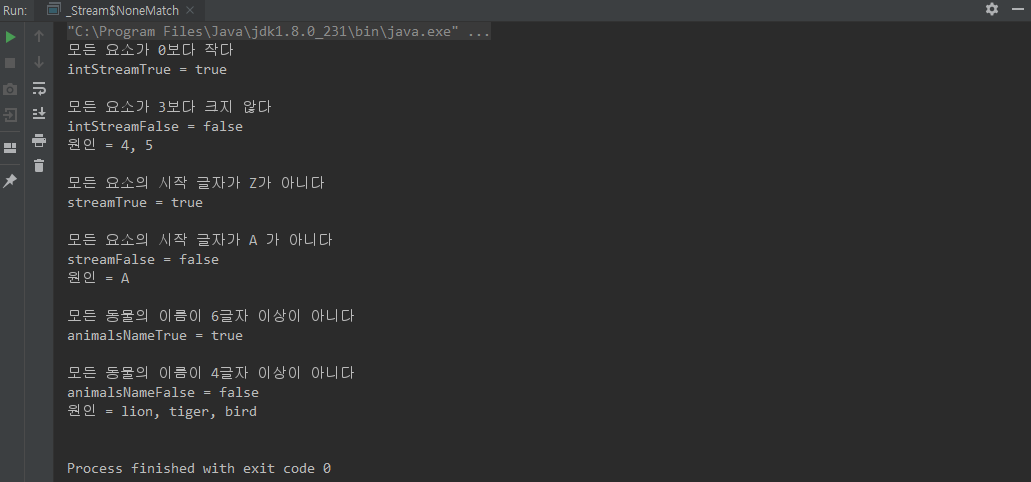
noneMatch(Predicate)
class NoneMatch {
static class Animal {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private Animal(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// IntStream NoneMatch True
boolean intStreamTrue = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.noneMatch(value -> value < 0);
System.out.println("모든 요소가 0보다 작다");
System.out.println("intStreamTrue = " + intStreamTrue);
System.out.println();
// IntStream NoneMatch False
boolean intStreamFalse = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.noneMatch(value -> value > 3);
System.out.println("모든 요소가 3보다 크지 않다");
System.out.println("intStreamFalse = " + intStreamFalse);
System.out.println("원인 = 4, 5");
System.out.println();
// Stream NoneMatch True
boolean streamTrue = Stream.of("AZ","BZ","CZ","DZ","EZ")
.noneMatch(value -> value.startsWith("Z"));
System.out.println("모든 요소의 시작 글자가 Z가 아니다");
System.out.println("streamTrue = " + streamTrue);
System.out.println();
// Stream NoneMatch False
boolean streamFalse = Stream.of("A","B","C","D","E")
.noneMatch(value -> value.startsWith("A"));
System.out.println("모든 요소의 시작 글자가 A 가 아니다");
System.out.println("streamFalse = " + streamFalse);
System.out.println("원인 = A");
System.out.println();
// animals NoneMatch True
boolean animalsNameTrue = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.noneMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() > 5);
System.out.println("모든 동물의 이름이 6글자 이상이 아니다");
System.out.println("animalsNameTrue = " + animalsNameTrue);
System.out.println();
// animals NoneMatch False
boolean animalsNameFalse = Stream.of(
new Animal(1L, "lion", 10),
new Animal(2L, "dog", 20),
new Animal(3L, "cat", 30),
new Animal(4L, "tiger", 40),
new Animal(5L, "bird", 50)
)
.noneMatch(animal -> animal.name.length() > 3);
System.out.println("모든 동물의 이름이 4글자 이상이 아니다");
System.out.println("animalsNameFalse = " + animalsNameFalse);
System.out.println("원인 = lion, tiger, bird");
System.out.println();
}
}
# 단점

익명클래스 >>>>>>> 자바 람다
참고 사이트
for-loop 를 Stream.forEach() 로 바꾸지 말아야 할 3가지 이유
for-loop를 Stream.forEach()로 바꾸지 말아야 할 3가지 이유 원문 : https://blog.jooq.org/2015/12/08/3-reasons-why-you-shouldnt-replace-your-for-loops-by-stream-foreach/ 간디작살! 소스 코드를 Java8로 바꾸자. 뭐든지 함수를 써
homoefficio.github.io
'03. JAVA > 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 18. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - Stream API 를 이용하여 2개의 배열 합치기 (0) | 2021.09.17 |
|---|---|
| 17. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - 인터페이스 default 메소드 정의하기 (0) | 2021.07.07 |
| 05. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - SOLID 원칙 (0) | 2020.09.06 |
| 09. 자바 8 (Java 8) - Collection 과 Map [미완성] (0) | 2020.08.31 |
| 11. 자바 8 (Java 8) - ObjectMapper, JsonPath, ModelMapper (1) | 2020.08.24 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
17. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - 인터페이스 default 메소드 정의하기
17. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - 인터페이스 default 메소드 정의하기
2021.07.07 -
05. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - SOLID 원칙
05. 자바 8 (JAVA 8) - SOLID 원칙
2020.09.06 -
09. 자바 8 (Java 8) - Collection 과 Map [미완성]
09. 자바 8 (Java 8) - Collection 과 Map [미완성]
2020.08.31 -
11. 자바 8 (Java 8) - ObjectMapper, JsonPath, ModelMapper
11. 자바 8 (Java 8) - ObjectMapper, JsonPath, ModelMapper
2020.08.24